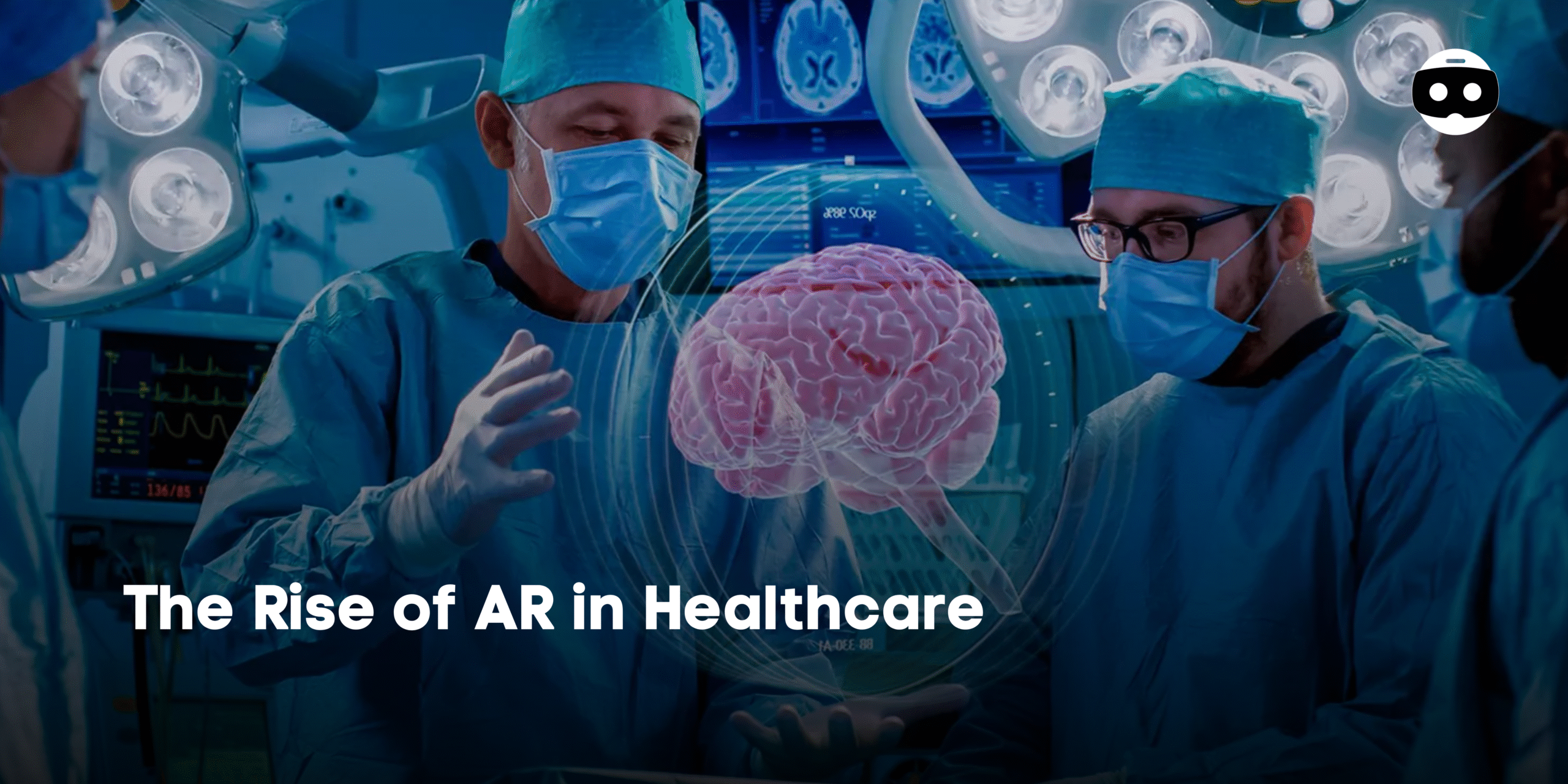
Augmented Reality (AR) is no longer only the stuff of sci-fi movies. In the healthcare domain, it’s increasingly becoming a bridge between virtual insights and real-world action. By overlaying digital information on physical environments, AR can enhance diagnosis, guide procedures, educate clinicians, and improve patient engagement. In this article, we explore real-world use cases, supporting evidence and case studies, challenges, and what’s ahead for AR in health.
Market Landscape & Growth Trajectory
- In 2025, the global AR in healthcare market is projected to reach USD 1.51 billion, with forecasts rising to USD 4.99 billion by 2030 (CAGR ~26.99 %)
- More broadly, the combined AR/VR healthcare market was valued at USD 3.4 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow steadily (CAGR ~16.8 %)
- Among AR/VR in healthcare, AR often commands a dominant share (for example, in certain segments, AR accounts for ~61 % of the market)
These figures reflect that many health organizations are moving from pilot projects to full deployments, especially in surgical guidance, training, and rehabilitation.
Use Cases & Case Studies
1. Surgery with Superhuman Precision
Performing surgery is like navigating a maze, one wrong move can have serious consequences.
Here’s where AR comes in.
In one trial, doctors used AR headsets that projected a 3D map of the patient’s internal organs while operating. This helped them insert surgical instruments more accurately cutting down mistakes by over 50%.
They also needed less X-ray radiation and completed the procedure faster.
In simple words: AR acted like a GPS for surgeons, showing exactly where to move their tools and what to avoid.
Another system tracked surgical instruments using small reflective dots that the AR headset could “see.” This allowed doctors to know the exact position of their instruments down to a fraction of a millimeter helping even young surgeons perform like seasoned experts.
2. Training the Next Generation of Doctors
Traditionally, medical students learn anatomy from textbooks or cadavers. But it’s hard to visualize how everything connects inside a living body.
AR is changing that.
Now, students can wear AR glasses or use tablets to see 3D organs floating in front of them, rotate them, zoom in, and even “walk around” to explore how the heart connects to veins or how muscles move.
Studies show that students who train with AR remember lessons better and make fewer errors when they start practicing.
It’s like going from reading about driving a car to actually sitting behind the wheel, only in a completely safe environment.
3. Helping Patients Heal Faster
Rehabilitation after surgery or injury can be slow and repetitive. AR turns this process into something interactive and motivating.
Patients can do exercises while an AR system shows whether they’re doing them correctly. Some hospitals use game-like AR programs, where patients earn points for proper movements, making recovery fun and measurable.
For people recovering from strokes or mobility issues, AR visuals can guide their limbs in real time, helping them re-learn correct movements.
Example: A patient sees a virtual outline of how to move their arm, and when they follow it correctly, the system gives instant feedback — just like a coach standing beside them.
4. Remote Support and Telemedicine
Imagine a rural doctor consulting with a specialist hundreds of miles away. Through AR glasses, the specialist can see exactly what the doctor sees and draw or highlight instructions directly in their view.
This means expertise can travel without the person having to, helping save time, costs, and even lives in emergencies.
In practice: a heart surgeon in Mumbai can guide a junior doctor in a smaller town through a live operation, step by step, using AR visuals.
Why AR Matters
| Benefit | What It Means for People |
| More accurate surgeries | Fewer mistakes, faster recovery times |
| Smarter training | Better-prepared doctors and nurses |
| Engaged patients | Faster healing and higher motivation |
| Remote care | Specialist support in every corner of the world |
| Cost savings | Fewer repeat procedures and shorter hospital stays |
The Challenges Ahead
Like any new technology, AR in healthcare still faces a few hurdles:
- It needs high accuracy even small visual mismatches could be risky in surgeries.
- AR devices are expensive, though prices are slowly dropping.
- Hospitals must ensure data privacy, since AR systems often use patient scans and real-time video.
- Training and approval take time ,doctors need to be comfortable with the tech, and regulators must ensure it’s safe.
The Future Looks Promising
As AR merges with AI and 3D medical imaging, it’s opening new frontiers:
- Doctors could one day see a real-time digital twin of the patient during surgery.
- Patients may use AR apps for home therapy, guided by virtual assistants.
- Medical wearables could project live health data right onto your skin’s surface, pulse, oxygen, and hydration in real time.
AR isn’t replacing doctors; it’s empowering them. And it’s giving patients more control, clarity, and confidence in their care.
Final Thoughts
From operating rooms to classrooms, AR is redefining how medicine is practiced, taught, and experienced.
It’s taking healthcare from reactive to proactive, making treatments safer, learning more immersive, and recovery more personal.
For a long time, healthcare relied on what doctors could see and touch. Now, thanks to AR, they can also see what was once invisible.